.jpg)
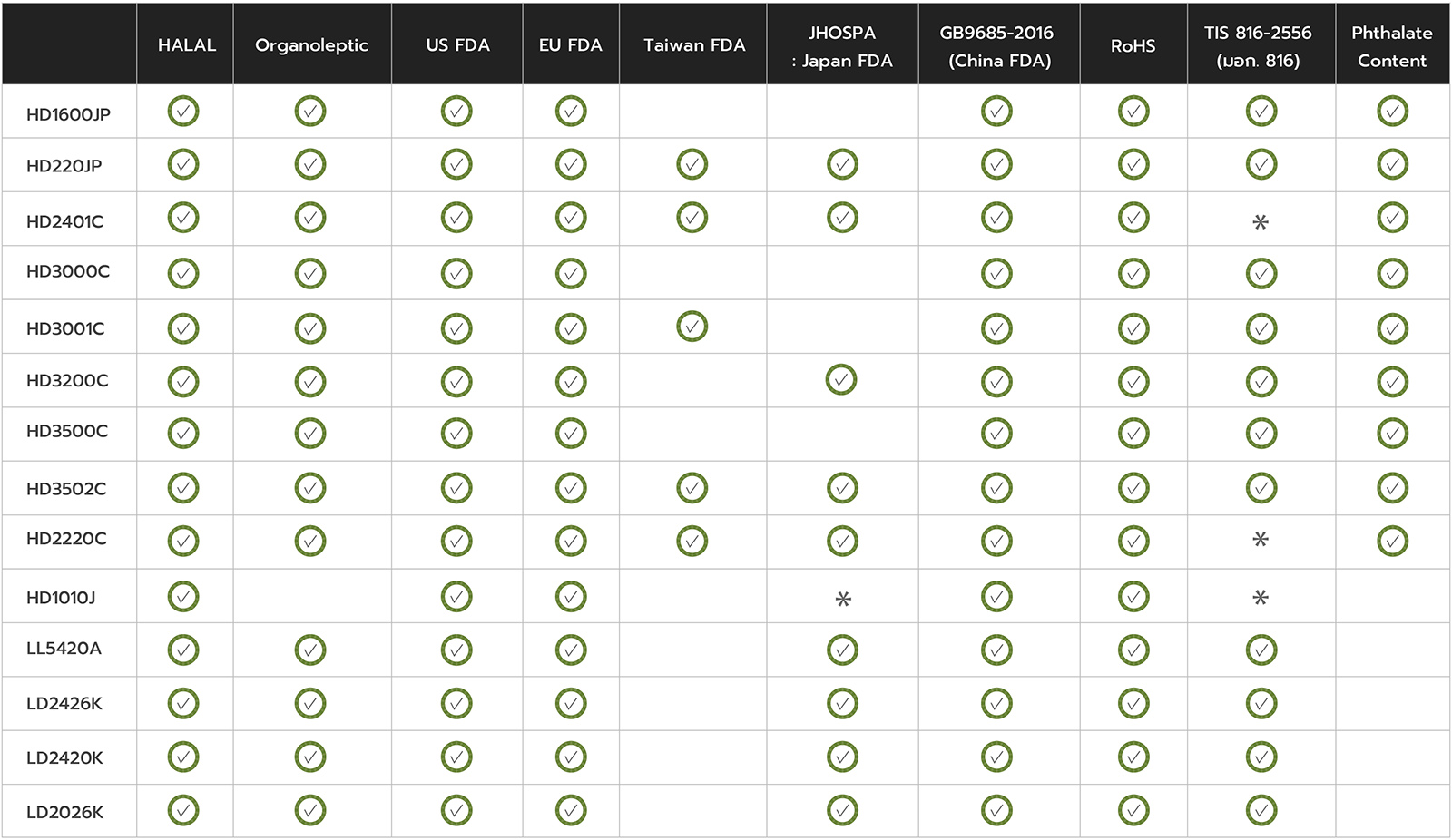
Halal
Islamic Law for Food Related Goods/Product


We manufacture plastic resins for caps and closures application for major business segments including beverage, food, home care, personal care and industrial markets.
We aim to contribute to the success of our customers based on strong innovation, concentrating on quality and efficiency, technical service and a global manufacturing platform.
We continue to develop the best quality products to enable business trends and consumer lifestyles to be more functional and sustainable.
Caps and closures product segments is divided into and for 5 main applications which are beverage, food and dairy product, personal care and beauty, home care and industrial.
These are beverages that do not contain dissolved carbon dioxide. Closures for such beverages have requirements that match converters and/or machines requirements. High density polyethylene or Polypropylene can be the material for this product




These are beverages that contain dissolved carbon dioxide. The process usually involves carbon dioxide under high pressure. Closures for such beverages require the material integrity to withstand the pressure within the bottle. High density polyethylene or Polypropylene can be the material for this product


These closures are used for liquid produced by the mammary glands of mammals such as cow’s milk or goat’s milk. Other products include water-based plant extracts such as soy milk, corn milk or almond milk. High density polyethylene or Polypropylene can be the material for this product

Closures are also used for flavoring garnishes, all types of sauces, monosodium glutamate (MSG), cooking sauces, ketchup, mayonnaise, mustard, oyster sauces, salad dressings, dips, pickled products, and other sauces, dressings and condiments. High density polyethylene or Polypropylene can be the material for this product

These closures are used for cooking oil, olive oil and vegetable oil of all kinds.

Polyethylene and polypropylene resin closures are used for types of all liquid, gels, foams, creams, body oil cleansers and mousses marketed for use in the shower. High density polyethylene or Polypropylene can be the material for this product

Closures that are used for toothpaste, toothbrushes, mouthwashes/dental rinses, denture care, mouth fresheners, at-home teeth whiteners, and dental floss. High density polyethylene or Polypropylene can be the material for this product

Closures for all hair care products, including shampoo, conditioner, colorants, styling, and hair loss treatments. High density polyethylene or Polypropylene can be the material for this product

Closures for a collection of facial care, body care and hand care products that does not include bath and shower and deodorant products. High density polyethylene or Polypropylene can be the material for this product

Closures for all aroma compound products used to give off scents. Polypropylene can be the material for this product

Closures for all detergent products used to clean crockery and cutlery. High density polyethylene or Polypropylene can be the material for this product

Closures for all products of spray/aerosol insecticides and other insecticides. Polypropylene can be the material for this product

Closures for laundry detergents, fabric softeners, and carpet cleaners. High density polyethylene or Polypropylene can be the material for this product

Closures for multi-purpose, bathroom, oven , kitchen, window/glass, and floor cleaners, descalers, drain openers, scouring agents and household antiseptics. Polypropylene can be the material for this product

Closures used for all industrial chemical container packaging. This includes chemical plastic drums and intermediate bulk containers. High density polyethylene or Polypropylene can be the material for this product


closures which consist of several parts where at least one part is integrated in the opening of the container and acts as the orifice of the container. High density polyethylene or Polypropylene can be the material for this product

These are closures with a system by which a push down action will either dispense the liquid from the container or reveal the opening orifice. Polypropylene can be the material for this product

These closures connect to the collar via a linkage or joint and open by a swinging mechanism. Low-density polyethylene, Linear low-density polyethylene or Polypropylene can be the material for this product

These are closures by which a single piece is used to close the container opening by latching on to the neck ring of the container. Low-density polyethylene, Linear low-density polyethylene can be the material for this product

These closures require a pushing action to seal the container's opening and a pulling action to completely remove the closure from the container. High density polyethylene or Polypropylene can be the material for this product

These are closures requiring a pull or thumb push action to allow the valve to open and water to flow through. High density polyethylene or Polypropylene can be the material for this product

These are round closures with a female thread that can be screwed onto a bottle. High density polyethylene or Polypropylene can be the material for this product

These are closures with a system by which an action on a lever will open a valve and allow water to flow through. High density polyethylene or Polypropylene can be the material for this product
1605284172.jpeg)
These closures have an opening that emits a mist of the product’s liquid. Polypropylene can be the material for this product


.jpg)
Islamic Law for Food Related Goods/Product
.jpg)
German Food Articles of Daily Use and Feed Code of September 1, 2005 (LFGB), Section 31 - Sensory Examination Odour and Taste Test
.jpg)
Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Specifications accordingto U.S. FDA 21 Code of Federal Regulations part 177.1520 (c) (2.1)
.jpg)
Plastic Materials and Articles Intended to Come into Contact with Food
.jpg)
Sanitation STD. for Food Utensils, Container and Package.

Japan Chemical Innovation and Inspection Institute
.jpg)
“The Hygienic Standards for Uses of Additives in Food Containers and Packaging Materials” under GB31603-2015
.jpg)
Restriction of Hazardous Substances: EU Directive 2011/65/EU
.jpg)
Polyethylene Industrial Standard
.jpg)
According to ASTM D3421-1975
.jpg)
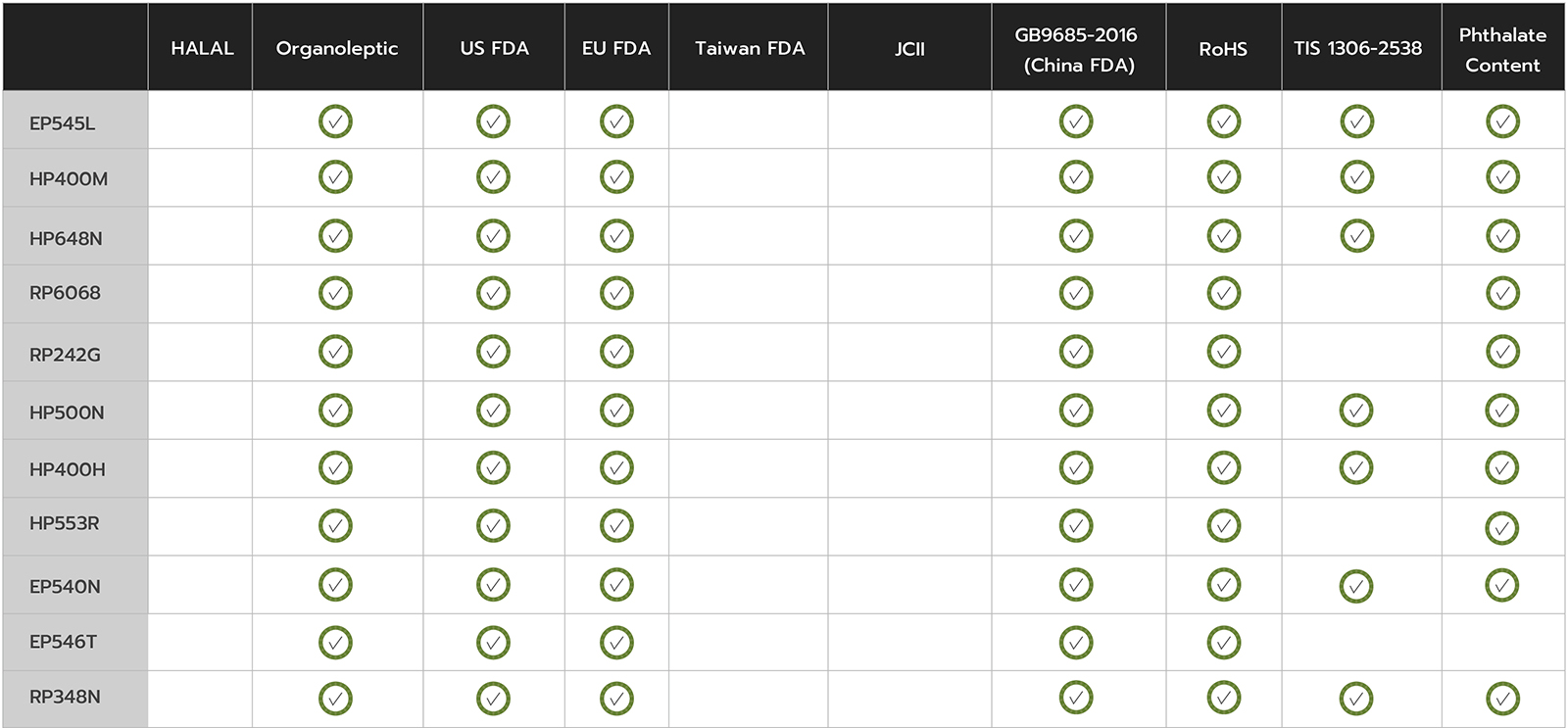
German Food Articles of Daily Use and Feed Code of September 1, 2005 (LFGB), Section 31 - Sensory Examination Odour and Taste Test
.jpg)
Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Specifications accordingto U.S. FDA 21 Code of Federal Regulations part 177.1520 (c) (2.1)
.jpg)
Plastic Materials and Articles Intended to Come into Contact with Food
.jpg)
“The Hygienic Standards for Uses of Additives in Food Containers and Packaging Materials” under GB31603-2015
.jpg)
Restriction of Hazardous Substances: EU Directive 2011/65/EU
* On process
Q : Decomposed material
A : Decrease heating
Q : Contamination and excessive regrind in a virgin/regrind blend
A : Reduce percentage of regrind (general rule- 25-30%)
Q : Contamination
A : Inspect resin for contamination and Purge machine thoroughly
Q : Long melt residence time
A : Reduce cycle time
Q : Improper gate size/location
A : Enlarge gate size and Relocate gate away from potential stress areas
Q : Material and mold temperature too high/low
A : Adjust material and mold temperature
Q : Injection/hold pressure too low
A : Increase injection/holding pressure
Q : Injection forward/boost time too short
A : Increase forward/boost time
Q : Fill speed too short/long
A : Adjust fill speed
Q : Cycle time too short
A : Increase cooling time
Q : Material density too high
A : Use lower density material
Q : Poor mold finish
A :
- Polish out undercuts in cavity
- Check any damaged surfaces
- Use mold-release agent
Q : Pressure too high / too long
A : Lower injection pressure, screw forward time or the injection boost time
Q : Cycle time too short
A : Increase cycle time
Q : Part to hot for ejection
A :
- Increase cooling time
- Decrease melt temperature
- Decrease mold temperature
Q : Too much packing
A : Lower injection pressure, screw forward time or the injection boost time
Q : Melt and/or mold temperature too high
A : Decrease melt/ mold temperature
Q : Screw speeds too High
A : Decrease the screw speed. High screw speeds may cause the material to degrade
Q : Material may have too much regrind content
A : Reduce percentage of regrind
Q : Insufficient pressure
A : Increase injection pressure
Q : Material and mold too cold
A : Reduce flow of cold water through mold
Q : Injection forward/boost time too short
A : Increase injection forward and boost time
Q : Fill speed to slow
A : Increase fill speed
Q : Runners/gates/nozzle too small
A : Check runners, gates and/or nozzle
Q : Insufficient number of gates
A : Increase number of gates
Q : Back pressure of entrapped air in mold
A : Incorporate or increase venting
Q : Mold and/or melt temperature too low
A : Use higher back pressure
Q : Non-uniformity of resin temperature
A : Change RPM
Q : Injection rate to low
A : Increase injection rate
Q : Air entrapment in mold
A : Increase venting
Q : Material/mold too cold
A : Increase material/mold temperature
Q : Too much mold surface lubricant
A : Use less mold surface lubricant
Q : Insufficient injection speed
A : Increase injection speed
Q : Material degraded in cylinder
A : Decrease heating
Q : Poor mold surface
A : Clean mold and/or polish
Q : Non-uniform feeding of material
A : Adjust temperature for optimum filling
Q : Insufficient packing of part
A : Increase shot size to maintain proper cushion
Q : Regrind levels inconsistent
A : Replace check valve if cushion cannot be maintained
Q : Melt pressure variations
A : Increase injection forward time and pressure to ensure gate freeze of
Q : Unbalanced runner system
A : - Increase holding pressure to maximum
A : - Increase injection rate
A : - Balance runner and gate sizes to provide balanced filling
Q : Melt temperature to low
A : Increase melt temperature
Q : Mold Temperature to low
A : Increase mold temperature
Q : Gate size to small
A : Increase gate size
Q : Non- uniform wall thickness
A : Redesign part for more uniform wall thickness to provide for optimum filling
Q : Mold closed too fast under too high pressure
A : Close mold slowly (punch and cavity)
Q : Mold improperly polished
A : Polish mold
Q : Material contain excessive moisture
A : Pre-heat mateia
Q : Mold too hot
A : Reduce temperature
Q : Insufficient pressure
A : Increase pressure
Q : Molding cycle too short
A : Increase time of cycle
Q : Mold too hot or too cool
A : Mold improperly polished
Q : Pressure too high/too long
A : Polish mold